
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a number of additional guidelines are in place for outdoor dining at Chester County restaurants. Please see Restore Chester County for specific information on outdoor dining with respect to Pennsylvania state guidelines.
How it Works
Outdoor dining is typically regulated as an accessory use to restaurants, breweries, wineries, and food trucks. Municipalities should enact rules and regulations to appropriately balance outdoor dining with the public's use of, and access to, outdoor public spaces. Outdoor dining typically occurs in the following locations:
Sidewalks
Sidewalks adjacent to restaurants are often used for outdoor dining. Outdoor dining located on sidewalks should ensure compliance with clear pedestrian zones and sight distances, ADA provisions, and other regulatory requirements.
Off-street Parking
Outdoor dining may be located in off-street parking areas. For example, outdoor dining may be permitted in underutilized parking areas adjacent to a restaurant.
Streetways
Municipalities may permit the use, or temporary use, of street cartways for outdoor dining. Examples of this include municipal approved conversion of on-street parking for outdoor dining for a neighboring restaurant, or the temporary restriction of vehicular access from roadways to permit the use of street right-of-way for outdoor dining and other pedestrian oriented events.
Special Events and Festivals
Outdoor dining is often a feature of community events and festivals. These special events may be coupled with the closure of streets to permit outdoor dining, or outdoor dining may occur as an accessory or pop-up use to support the special event. Outdoor dining associated with special events are not limited to restaurants and may also support food trucks, breweries, or wineries.
Benefits
Neighborhood Vibrancy and Placemaking
Outdoor dining has become increasingly popular, particularly for establishments located in downtown locations, planned developments, or unique locations. Outdoor dining helps to define a neighborhood's character and sense of place by offering place-driven experiences allowing restaurant patrons to connect with their neighborhoods.
Street Activation
Outdoor public spaces such as sidewalks become enlivened when restaurant patrons dine outdoors. Public spaces may be further benefited through streetscaping often associated with outdoor dining. Activating public spaces makes the neighborhood more viable and can help to foster a sense of community and safety of streets by encouraging a mixture of uses and street vitality at the pedestrian scale.
Economic Development
The desirability of outdoor dining may contribute to a location's economic development and the resiliency of local businesses by offering diverse and exciting options for restaurant diners. Outdoor dining can be combined with other economic development techniques such as community events, or the strategic closure of streets for vehicular access to allow for larger scale outdoor dining and pedestrian oriented use of neighborhood streets.
Consumer Choice
Open air dining may be more appealing than traditional indoor dining for a number of reasons. For example, outdoor dining may be appealing to families looking for a more casual atmosphere to dine with young children, or for pet owners to dine with their leashed dogs.

Municipalities can support outdoor dining by establishing specific standards in their zoning ordinance, land development ordinance, or municipal code.
Get Started
Outdoor dining can be regulated in a number of ways. The following are ways which municipalities can approach the regulation of outdoor dining:
Zoning Ordinance
Regulating outdoor dining through a municipality's zoning ordinance is one of the most restrictive regulatory means of permitting outdoor dining. Regulating outdoor dining by zoning ordinance allows the municipality to specify zoning districts where outdoor dining is permitted while setting specific standards for the permission of outdoor dining. At a minimum, the zoning ordinance should permit outdoor dining as a use by-right. Requirements for outdoor dining could be placed in zoning, or deferred to the municipal code or permit for more flexibility as described below.
Regulation through the zoning ordinance would require variances to be approved by the municipal Zoning Hearing Board for deviations from defined ordinance standards, offering the municipality a high level of regulatory control. This option however, is the least flexible for making modifications to the ordinance, as public hearings and notifications would be required for ordinance modification.
Municipal Code
Outdoor dining regulated through the municipal code or by a standalone ordinance offers more flexibility than regulating outdoor dining through the zoning ordinance and eliminates the need for variance requests which can be a time consuming process.
Permit
The most flexible method for municipalities to regulate outdoor dining is through an administrative permit. Municipal staff approval of permits for outdoor dining allows for the process to be more approachable to applicants, allows for ongoing communication between the municipality and the applicant, and is a more timely method of permitting outdoor dining facilities.
Municipalities can support outdoor dining through setting specific and clear standards. At the regulatory level, municipalities may encourage opportunities for outdoor dining in zoning and land development ordinances as well as municipal codes. Zoning and land development provisions should be evaluated to permit design features which promote outdoor dining. The development of design guidelines for outdoor dining may be helpful to illustrate various permitting requirements for outdoor dining. Examples of outdoor dining features to evaluate through these regulations include: zoning districts permitting outdoor dining, ADA compliance, acceptable dining barriers, clear pedestrian and sidewalk zones, and streetscaping standards.
Considerations
Regulation Requirements
Without clearly defined standards and regulations for outdoor dining, regulatory requirements may seem overwhelming or unclear to potentially interested restaurants. Clearly defined regulations may help to minimize uncertainty for the applicant and minimize issues with enforcement. Municipalities should ensure that adequately descriptive and illustrative standards are set for outdoor dining and that permitting requirements are clearly defined.
Encroachment Permitting
A specific item for municipalities to consider is the permission needed for the encroachment of outdoor dining into areas owned by an entity other than the restaurant, which is a common occurrence in outdoor dining. The permitting process should clearly indicate property owners, potential locations of encroachments, and should require specific permissions for these potential encroachments by the property owner.
Neighborhood Compatibility
The street level scale of outdoor dining needs to be balanced with overall neighborhood compatibility. Items frequently of concern to neighborhood residents include: hours of operation, noise, lighting, pedestrian access, trash, customer behavior, and potential competition for outdoor public space. Regulatory standards should be developed while taking into account these concerns, and should ensure that outdoor dining is compliant with the overall needs of the community and that potentially disruptive activities are adequately buffered from adjacent residential uses.
Access to Sanitary Facilities
Establishments offering outdoor dining may have a need for a number of different types of sanitary facilities, such as hand washing or beverage preparation stations for employees, or bathrooms for customers. The placement of sanitary facilities should be addressed during the permitting process, with special emphasis placed on public health standards and neighborhood compatibility.
Safety and Access
Outdoor dining on sidewalks and along roadways may create conflicts between vehicles, pedestrians, and restaurant patrons. Permitting requirements should include extensive requirements covering barriers between sidewalks and roadways, and plans should be approved by municipalities which illustrate clear pedestrian and sidewalk zones. Safety measures such as barriers should be regulated to ensure that they meet building code requirements and that they complement the visual character of the surrounding neighborhood.

Kennett Square Borough — Third Thursday on State
The Third Thursday event in Kennett Square Borough is held in summer months; State Street in the borough is closed to vehicular traffic to allow for outdoor dining, extended shopping hours, live music, and children's activities. Third Thursday is regulated by Kennett Square through a permit process and with respect to PennDOT regulations.
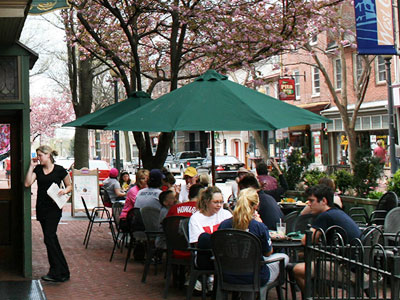
West Chester Borough — Outdoor Dining
West Chester Borough permits outdoor dining in the Town Center zoning district. Requests for outdoor dining are regulated through a permit process which requires the applicant to submit information such as location of the dining area, seating plan, pedestrian requirements, and streetscaping requirements.

Media Borough — Dining Under the Stars
Dining Under the Stars is a popular summer pastime in Media Borough. The borough closes State Street to vehicular traffic to allow for outdoor dining, shopping, and socialization. Dining Under the Stars is regulated by Media Borough through a permit process, and in accordance with PennDOT requirements.


